Exploring the World of Web3, Safety First, Users Must Remember These 3 Safety Rules: Do not fill in mnemonic phrases/private keys on any webpage, be cautious when clicking on wallet transaction interfaces’ confirmation buttons, and be aware that links obtained from Twitter/Discord/search engines may be phishing links.
As we enter a new cycle, the risks of online interactions on the blockchain increase as user activity grows. Phishers usually employ methods such as creating fake wallet websites, stealing social media accounts, creating malicious browser extensions, sending phishing emails and information, and releasing fake applications to deceive users into disclosing sensitive information, resulting in asset losses. Phishing forms and scenarios exhibit characteristics such as diversity, complexity, and stealth.
For example, phishers typically create fake websites that resemble legitimate wallet websites to trick users into entering their private keys or mnemonic phrases. These fake websites are often promoted through social media, email, or advertisements, misleading users into thinking that they are accessing legitimate wallet services, thus stealing their assets. Additionally, phishers may use social media platforms, forums, or instant messaging applications to impersonate wallet customer service or community administrators and send users false messages requesting wallet information or private keys. This method exploits users’ trust in official channels to persuade them to disclose personal information.
Advertisements – Continued in the next section




In summary, these cases highlight the threat of phishing to Web3 wallet users. To help users enhance their awareness of Web3 wallet security and protect their assets from loss, OKX Web3 conducted in-depth community research and collected numerous phishing incidents experienced by Web3 wallet users, extracting the four most common phishing scenarios encountered by users. Through detailed examples in different scenarios, OKX Web3 has written the latest guide on how Web3 users can conduct secure transactions, combining text and graphics, for everyone to learn and reference.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Malicious Information Sources
1. Replies to Popular Project Tweets
2. Stealing Official Twitter/Discord
3. Google Search Ads
4. Fake Applications
5. Countermeasures: OKX Web3 Wallet Supports Phishing Link Detection and Risk Reminders
Wallet Private Key Security
1. Interacting with Projects or Qualification Verification
2. Impersonating Project Customer Service or Administrators
3. Other Possible Ways of Leaking Mnemonic Phrases/Private Keys
4 Classic Phishing Scenarios
Scenario 1: Stealing Main Chain Tokens
Scenario 2: Transferring to Similar Addresses
Scenario 3: On-Chain Authorization
Scenario 4: Off-Chain Signature
Other Phishing Scenarios
Scenario 6: Solana Tokens and Account Permissions
Scenario 7: EigenLayer Call queueWithdrawal
Exploring the World of Web3, Safety First
Malicious Information Sources
1. Replies to Popular Project Tweets
Replying to popular project tweets is one of the main ways malicious information is spread. Phishing Twitter accounts can make their logos, names, and verification badges identical to official accounts, and even have tens of thousands of followers. The only way to differentiate between them is through their Twitter handles (pay attention to similar characters), so users must be vigilant.


Additionally, fake accounts often deliberately reply to official tweets, but their replies contain phishing links, easily leading users to believe that they are official links, thus falling victim to scams. Currently, some official accounts add “End of Tweet” to their tweets, reminding users of the risk of phishing links in subsequent replies.


2. Stealing Official Twitter/Discord
To increase credibility, phishers also steal project or KOL’s official Twitter/Discord accounts and release phishing links in the name of the official accounts, making it easy for many users to fall for the scams. For example, Vitalik’s Twitter account and the official Twitter account of TON project have been previously compromised, allowing phishers to release false information or phishing links.



3. Google Search Ads
Phishers sometimes use Google search ads to publish malicious links. The names displayed in the browser make them appear as official domains, but when clicked, they redirect to phishing links.


4. Fake Applications
Phishers also lure users through fake applications, resulting in users’ private keys being leaked and assets being lost. Phishers have modified Telegram installation packages in the past, changing the on-chain addresses for receiving and sending tokens, resulting in users losing their assets.




5. Countermeasures: OKX Web3 Wallet Supports Phishing Link Detection and Risk Reminders
Currently, OKX Web3 Wallet supports phishing link detection and risk reminders to help users better cope with the aforementioned issues. For example, when users access websites using their browsers with the OKX Web3 extension wallet, if the domain is a known malicious domain, they will receive an alert immediately. In addition, if users use the OKX Web3 APP to access third-party DApps on the Discover interface, the OKX Web3 Wallet will automatically perform risk detection on the domain. If it is a malicious domain, it will intercept and remind users, prohibiting their access.




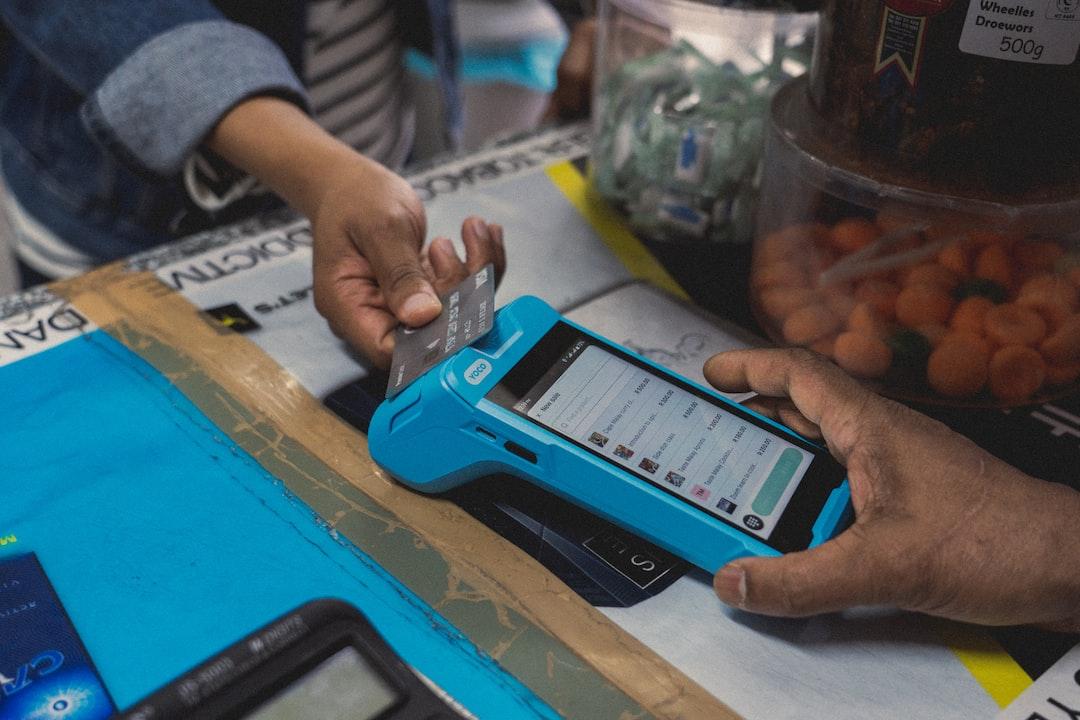
1. Interacting with Projects or Qualification Verification
Phishers often disguise themselves as pop-up windows of browser extensions or other web pages when users are interacting with projects or undergoing qualification verification, requesting users to fill in mnemonic phrases/private keys. These are usually malicious websites, and users should be vigilant.




2. Impersonating Project Customer Service or Administrators
Phishers often impersonate project customer service or Discord administrators and provide URLs for users to enter mnemonic phrases or private keys. In such cases, the other party is a phisher.




3. Other Possible Ways of Leaking Mnemonic Phrases/Private Keys
There are many possible ways for users’ mnemonic phrases and private keys to be leaked, including computer infection with Trojan horse malware, using fingerprint browsers intended for private browsing, using remote control or proxy tools on the computer, storing mnemonic phrases/private keys screenshots in the photo album that are uploaded maliciously by a fake app or backed up to the cloud, but the cloud platform is compromised, monitoring the process of entering mnemonic phrases/private keys, people around obtaining mnemonic phrase/private key files/papers, and developers pushing private key code to Github, etc.
In conclusion, users need to securely store and use their mnemonic phrases/private keys to ensure the security of their wallet assets. Currently, as a decentralized self-custodian wallet, OKX Web3 Wallet offers multiple backup methods for mnemonic phrases/private keys, including iCloud/Google Drive cloud storage, manual backup, and hardware backup. It has become one of the wallets in the market that supports a comprehensive range of private key backup methods, providing users with a more secure way to store private keys. Regarding the issue of private key theft, OKX Web3 Wallet supports mainstream hardware wallets such as Ledger, Keystone, and Onekey, ensuring that the private keys of hardware wallets are stored in the hardware wallet device, controlled by the users themselves, thus safeguarding asset security. In other words, OKX Web3 Wallet allows users to securely manage their assets through hardware wallets while freely participating in on-chain token trading, NFT markets, and various dApp project interactions. Furthermore, OKX Web3 Wallet has now launched MPC non-private key wallets as well as AA smart contract wallets, helping users simplify private key issues further.
4 Classic Phishing Scenarios
Scenario 1: Stealing Main Chain Tokens
Phishers often name malicious contract functions as “Claim,” “SecurityUpdate,” or other enticing names, but the actual function logic is empty, only transferring the user’s main chain tokens. Currently, OKX Web3 Wallet has launched the transaction pre-execution function, displaying the asset and authorization changes on the chain for the transaction, further reminding users to pay attention to security. Additionally, if the interaction contract or authorization address is a known malicious address, a red security reminder will be given.




Scenario 2: Transferring to Similar Addresses
When large transfers are detected, phishers generate and receive addresses with the first few digits identical to the user’s address, using “transferFrom” to perform zero-value transfers or using fake USDT to perform transfers of a certain amount, contaminating the user’s transaction history. They hope that the user will mistakenly copy the wrong address from the transaction history for subsequent transfers, completing the scam.




Scenario 3: On-Chain Authorization
Phishers often induce users to sign “approve/increaseAllowance/decreaseAllowance/setApprovalForAll” transactions and upgrade to pre-calculated new addresses using Create2, bypassing security checks to deceive users into granting authorization. OKX Web3 Wallet provides security reminders for authorization transactions, and users should pay attention to the fact that the transaction is related to authorization and be aware of the risks. Additionally, if the authorized address is a known malicious address, a red information reminder will be given to prevent users from falling for the scam.


Scenario 4: Off-Chain Signature
In addition to on-chain authorization, phishers also use off-chain signature to conduct phishing activities. For example, ERC20 token authorization allows users to authorize a certain amount to another address or contract, and the authorized address can transfer the user’s assets using “transferFrom,” which phishers exploit for fraud. Currently, OKX Web3 Wallet is developing a risk alert feature for such scenarios. When users sign an offline signature, the signing authorization address will be parsed, and if it matches a known malicious address, a risk reminder will be given to the user.
Other Phishing Scenarios
Scenario 5: TRON Account Permissions
This scenario is relatively abstract. Phishers obtain users’ TRON account permissions to control their assets. TRON account permissions are similar to EOS and are divided into Owner and Active permissions. They can be set up as multi-signature forms for permission control. For example, the Owner threshold is set to 2, with two addresses having weights of 1 and 2, respectively. The first address is the user’s address with a weight of 1, unable to operate the account independently.




Scenario 6: Solana Tokens and Account Permissions
Phishers modify the ownership of ATA token accounts through SetAuthroity, effectively transferring the tokens to a new owner address. Once users are phished through this method, their assets are transferred to the phishers, and so on. Additionally, if users sign an Assign transaction, the ownership of their regular accounts will be changed from the System Program to a malicious contract.


Scenario 7: EigenLayer Call queueWithdrawal
Due to the design mechanisms of the protocol itself, this scenario is also easily exploited by phishers. Based on the Ethereum middleware protocol EigenLayer’s queueWithdrawal call, it allows specifying another address as the withdrawer, and users who fall for the phishing scheme sign this transaction. After seven days, the specified address obtains the user’s pledged assets through completeQueuedWithdrawal.
Exploring the World of Web3, Safety First
Safely using Web3 wallets is crucial for protecting assets. Users should take preventive measures to mitigate potential risks and threats. They can choose the industry-leading and security-audited OKX Web3 Wallet to explore the world of Web3 more securely and conveniently.
As the most advanced and feature-rich wallet in the industry, OKX Web3 Wallet is completely decentralized and self-custodian. It supports a one-stop experience for users to explore on-chain applications. It currently supports 85+ public chains and maintains consistency across the app, browser extension, and web versions, covering wallets, DEX, DeFi, NFT markets, and DApp exploration in five major categories. It also supports Ordinals market, MPC, and AA smart contract wallets, gas exchange, and hardware wallet connection. Additionally, users can enhance wallet security by securely storing and protecting their private keys and mnemonic phrases, regularly updating wallet applications and operating systems, handling links and information cautiously, and enabling multi-factor authentication.
In conclusion, in the world of Web3, asset security is paramount. Users must remember these three Web3 safety rules: Do not fill in mnemonic phrases/private keys on any webpage, be cautious when clicking on wallet transaction interfaces’ confirmation buttons, and be aware that links obtained from Twitter/Discord/search engines may be phishing links.
OKX Web3


Further Reading
Upgrading to Cancun initiates the era of fee reduction. How to fully explore Ethereum and L2 ecosystems through OKX Web3 Wallet?
OKX Wallet | The industry’s first BRC-20 wallet! OKX Web3 multi-chain wallet supports BRC-20 transactions.

